body parts of honeybee
18 Body Parts of Honeybee – What Amazing Things They Do!
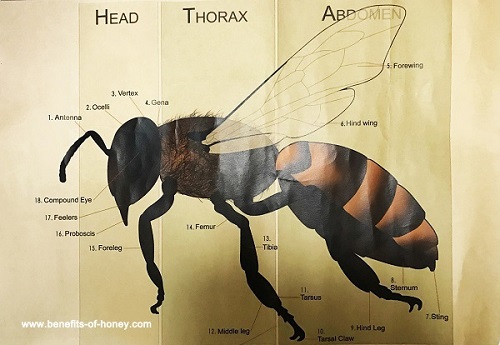
1. Antenna: Enables the honeybee to smell, detect the direction of odor, and even calculate the speed of flight.
2. Ocelli: Acts as a photo receptor, detecting changes in light intensity and direction; helps the bee with sun orientation so they can navigate well during the day.
3. Vertex: Top of the honeybee’s head where the three ocelli (simple eyes) are.
4. Gena: The sides of the head, just below the eyes and somewhat like human cheeks.
5. Forewing: Wing closest to the head, typically larger than its hindwing; it’s main function is flight but it also is used as a cooling mechanism.
6. Hind Wing: Wing furthest from the head; it’s main function is flight but it is also used to fan away heat and cool the hive.
7. Sting: a sharp organ at the end of the bee’s abdomen used to inject venom; once a honey bee stings, it also loses its life. The honeybee leaves the sting in the body of the victim and when pulling away ruptures the abdomen and dies.
8. Stemum: The underside of the abdomen.
9. Hind Leg: One of a set of legs furthest from the head. Also where workers have a unique set of tools used to collect and carry pollen called the comb, press, rakes, and basket.
10. Tarsal claw: Found at the end of the leg; responsible for clasping onto rougher surfaces and surrounded at its base by several short stiff bristles.
11. Tarsus: The last segment of the leg; primarily responsible for forward and backward movement.
12. Middle Leg: Leg located between the foreleg and hind leg.
13. Tibia: Fourth segment of an insect leg; primarily responsible for forward and backward movement.
14. Femur: Third segment of an insect leg; primarily responsible for forward and backward movement.
15. Foreleg: Leg closest to the head.
16. Proboscis: Tube-like mouth part used to suck up nectar, honey, and water, and exchange food between bees.
17. Feelers: Tiny antenna-like structures that have sensory hairs used to detect nectar and identify flowers, water, and the colony.
18. Compound Eye: Arthropod eye made of 6,900 tiny lenses called facets which are in groups called ommatidia connected to the optic nerve. The images from the thousands of lenses join together in the honeybee’s brain, allowing the bees to have excellent detection of color, polarized light and motion.
Other Related Pages on Body Parts of Honeybee
1. Honey is perceived as vomit by some people as it comes out from the bee’s mouth. More in: Honey is Bee Vomit, Legit? Absolutely Not, Honeybee has 2 Stomachs!
2. Do bees poop in the honey they make? Are their droppings smelly when all they eat is honey and pollen? What do honey bees use to make the bee hive? Is it true that the government is using bees to sniff out bombs? Get these answers and fun facts of honey bee in Bee & Honey Questions Answered.
3. Learn about this little busy creature’s extraordinary abilities: 20 Wonderful Honey Bee Facts (#8 is Surprising).